China’s electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is undergoing a structural transformation from asset-heavy ownership models toward service-oriented frameworks. Charging-as-a-Service (CaaS), characterized by subscription-based access, third-party operation, and fleet-centric service-level agreements, has emerged as a key commercialization pathway. According to market estimates published by Mordor Intelligence, the China EV Charging-as-a-Service market is projected to expand from USD 70.54 million in 2025 to USD 222.96 million by 2030, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.88%. This paper synthesizes the market size, segmentation, demand drivers, constraints, and competitive dynamics of China’s CaaS sector, and interprets its implications from an international and U.S.-oriented analytical perspective.
EV Charging-as-a-Service refers to a business model in which charging infrastructure is financed, deployed, operated, and maintained by specialized service providers, while end users—typically fleets, enterprises, property owners, or municipalities—pay through subscriptions, contracted capacity, or usage-based tariffs. Unlike traditional owner-operator charging models, CaaS emphasizes operational uptime, energy management, and digital service layers rather than hardware ownership.
In China, this model has gained particular relevance due to the scale of fleet electrification, high urban vehicle density, and policy-supported infrastructure deployment. Mordor Intelligence identifies CaaS as one of the fastest-growing segments within China’s EV charging ecosystem during the 2025–2030 forecast period (Mordor Intelligence, 2024).
The China EV Charging-as-a-Service market reached an estimated value of USD 70.54 million in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 222.96 million by 2030. The implied CAGR of 25.88% significantly exceeds that of conventional EV charging hardware markets, reflecting the shift from one-time equipment sales to recurring service revenues (Mordor Intelligence, 2024).
Despite rapid growth, the market remains relatively small in absolute USD terms compared with China’s total EV charging infrastructure investment. This indicates that CaaS is still in an early commercialization phase, with growth driven primarily by institutional fleets rather than mass consumer adoption.
AC chargers accounted for the largest share of the CaaS market in 2024, representing over half of installed capacity. Their dominance is attributed to lower capital expenditure, compatibility with overnight depot charging, and minimal grid upgrade requirements. However, DC fast chargers are projected to exhibit faster growth through 2030, supported by logistics fleets that require rapid turnaround and daytime opportunity charging (Mordor Intelligence, 2024).
Company vehicles and centralized motor pools represented the largest fleet segment in 2024, benefiting from predictable parking patterns and centralized energy management. In contrast, delivery and logistics fleets are identified as the fastest-growing segment, driven by the expansion of same-day and next-day e-commerce delivery services. Mordor Intelligence projects this segment to achieve a CAGR exceeding 28% through 2030, reflecting the operational necessity of guaranteed charging access for high-utilization vehicles.
Low-power systems below 22 kW (Level 1 / AC) held the largest market share in 2024, consistent with overnight depot use cases. However, chargers above 150 kW represent the fastest-growing power category, aligned with the adoption of high-voltage EV architectures and the operational requirements of long-haul logistics and premium passenger fleets.
Public charging setups accounted for approximately two-thirds of the market in 2024, benefiting from mixed user traffic and higher utilization rates. Semi-public installations—such as logistics parks, business campuses, and controlled-access depots—are expected to grow at a higher rate, as they combine guaranteed fleet access with partial public monetization (Mordor Intelligence, 2024).
One of the primary structural drivers of China’s CaaS market is the rapid electrification of logistics and delivery fleets. China’s courier sector processed more than 170 billion parcels in 2024, reinforcing demand for reliable overnight and depot-based charging solutions. Under these conditions, fleets increasingly favor subscription-based charging contracts that guarantee availability and uptime, supporting long-term revenue stability for CaaS providers.
Policy support and infrastructure investment also contribute materially to market growth. National and local initiatives aimed at improving charging availability, particularly in urban and highway corridors, reduce deployment barriers and accelerate service rollout. Mordor Intelligence highlights public-private partnership (PPP) models as an enabling mechanism for semi-public charger deployment, especially in transport hubs and expressway service areas.
Finally, digital optimization—such as AI-enabled load balancing, smart scheduling, and dynamic pricing—enhances asset utilization and mitigates peak electricity costs. These software-driven capabilities differentiate CaaS offerings from standalone charging hardware and strengthen customer retention.
Despite strong growth prospects, the CaaS market faces several structural constraints. Electricity price volatility, particularly under China’s evolving market-based power pricing reforms, introduces margin risk for fixed-rate subscription models. Operators without access to hedging instruments or flexible pricing mechanisms may experience profit compression.
Urban grid congestion presents an additional challenge, especially in tier-1 cities where transformer capacity and interconnection timelines can delay deployment and increase capital costs. Mordor Intelligence identifies distribution infrastructure limitations as a key restraint on near-term expansion in dense urban cores.
Competitive pressure from OEM-integrated charging networks also poses a risk. Vehicle manufacturers operating proprietary or semi-closed charging ecosystems can divert utilization away from independent CaaS providers, particularly in premium vehicle segments.
The China EV Charging-as-a-Service market is characterized as moderately concentrated. Major operators identified by Mordor Intelligence include TELD, StarCharge, State Grid EV Service, YKC, and NIO Power. Competitive advantage in this market is increasingly defined by access to grid resources, fleet contracts with service-level guarantees, and advanced energy management capabilities rather than charger count alone.
OEM participation and vertical integration continue to intensify competition, while regulatory emphasis on interoperability limits the potential for monopolistic lock-in. Industry consolidation is expected as scale becomes critical for managing power procurement risk and technology upgrades.
From 2025 to 2030, China’s EV Charging-as-a-Service market is expected to transition from early growth to structural scaling. While public charging will remain dominant in volume terms, value creation is likely to concentrate in fleet-oriented, semi-public, and high-utilization service models.
For international observers and U.S. stakeholders, China’s CaaS market serves as a reference case for fleet-driven monetization, subscription-based charging economics, and the integration of energy management into mobility services. However, differences in regulatory frameworks, electricity markets, and urban density suggest that direct replication outside China requires localized adaptation.
Mordor Intelligence. China EV Charging-as-a-Service Market – Growth, Trends, and Forecasts (2025–2030).
Available at: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/china-ev-charging-as-a-service-market
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry

Ecogenix 2-in-1 CCS & J1772 to Tesla Adapter One Adapter for Level 1, Level 2 & Level 3 Charging Freedom...

Lectron J1772 to Tesla Adapter (80 Amp, 250V) High-Power NACS Adapter for Everyday AC Charging As North America continues transitioning...
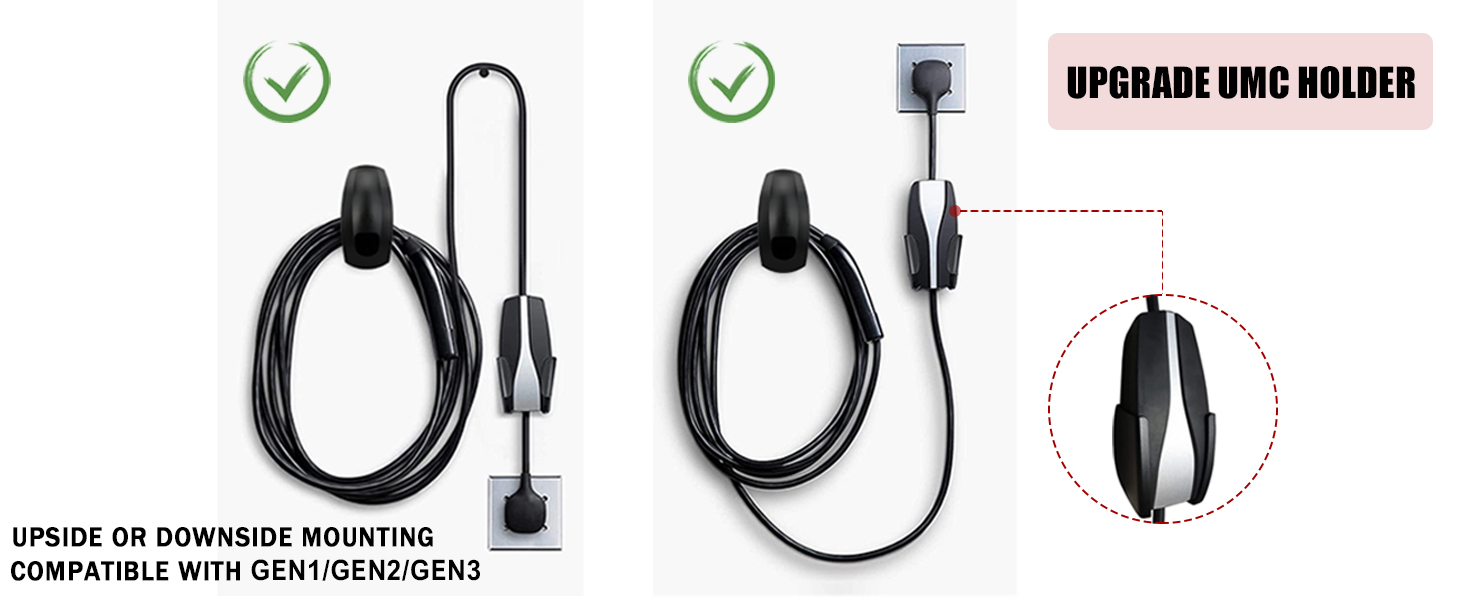

SEVEN SPARTA Tesla Charging Cable Holder with Chassis Bracket A Clean, Safe, and Durable Garage Charging Solution A common issue...